
Getting Started with Azure Key Vault
Table of Contents
Please check here for scripts using the latest PowerShell cmdlets.
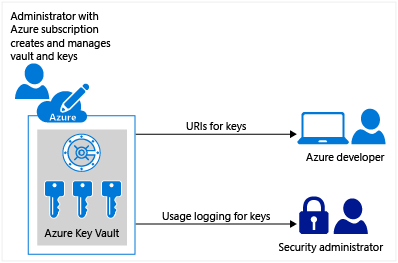
Azure Key Vault service is a cloud hosted, HSM(Hardware Security Modules)-backed service for managing cryptographic keys and other secrets. With Azure Key Vault, the process of managing and controlling the keys required for an application or multiple applications for an enterprise can be handled at a centralized place. Also these sensitive information no longer needs to be exposed in the application's configuration file or in database. Keys can be created in the vault and accessed via url's by the required application. Operations against the Key Vault are authenticated and authorized using Azure Active Directory. So in short all that a developer would need to know are the URI's for the keys, the sdk/api to access the vault features and also on the mechanism to authenticate against the AD application (an appId/client secret or appId/certificate).
Key Types
The initial release of Azure Key Vault only supports RSA keys (asymmetric cryptography) - it supports both software and HSM processed keys, and are represented as JSON Web Key objects. In future there might be more support for the different key types that are there in cryptography. For those who are new to cryptography or needs a quick recap on cryptography algorithms:
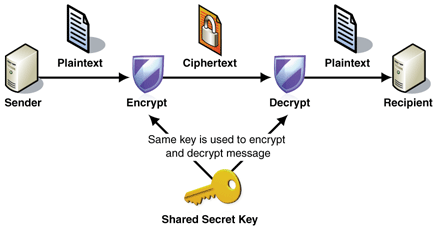
Symmetric Cryptography
Symmetric cryptography, uses the same key to encrypt and decrypt the data. The keys are shared between the identities that require to transfer the encrypted data.
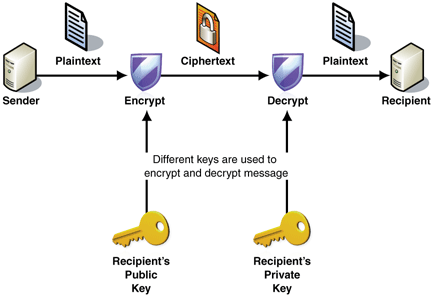
Asymmetric Cryptography
Asymmetric cryptography, also known as public key cryptography uses two separate keys - a public key and private key. The public key can be used to encrypt the data or to verify a digital signature whereas the private key is used to decrypt the text or to digital sign.
To create a new key in the Azure Key Vault, first we need to create the vault, using powershell scripts. You would need to install azure module version 0.8.13 version or higher for the key vault scripts to execute. Detailed steps on creating the vault and keys is documented here. Once we have the key created we can get the attributes of the key, using Get-AzureKeyVaultKey. This is as per the JSON Web Key(JWK) format. The 'n/e' values in the below key are for the RSA key type(kty), showing the public key information.
PS C:\> Get-AzureKeyVaultKey -Name rahulkey -VaultName testvaultrahul
Attributes : Microsoft.Azure.Commands.KeyVault.Models.KeyAttributes
Key : {"kid":"https://testvaultrahul.vault.azure.net/keys/rahulkey/0f653b06c1d94159bc7090596bbf7784","kty":"RSA","key_ops":["encrypt","decrypt","sign","verify","w
rapKey","unwrapKey"],"n":"xAXdHg5IAiU44GLM41hrCgfbEf8vg414lwIXBRHwPH-GTdQo3x5hMyvEtT26udcWLeRDDYGQxquuQ03ChXmXaE1Z8rdDpuaciJVoTB8wA_icr4Ww4ld0zuk9Nf31sVP-T_
UiYBpg_3MdwbDvO53udtknLWnXEa-Y-NXlCwUus6LOtfoG1_oVg5B5OFfcW993Zb44C3ZMoOESa-fW0eT6OefBJOgXwGG5gB-zAB2D7uzhStu3Cp4OiFELQSAS4gpt2GCUI76YkTfq8jnIJ7bi5cYzUb-Sv2
9nkiwJV9I7hN6wuoz1gNRoJJVisBtidiFd8EYYuCGB3AH8OWbWS_sXEw","e":"AQAB"}
VaultName : testvaultrahul
Name : rahulkey
Version : 0f653b06c1d94159bc7090596bbf7784
Id : https://testvaultrahul.vault.azure.net/keys/rahulkey/0f653b06c1d94159bc7090596bbf7784
Key Operations
Now that we have a key in the vault, we can use this to perform different operations allowed on the key, as provided in the key_ops field in the key details above. Typical operations that can be performed using the key are Encrypt, Decrypt, Sign, Verify, WrapKey and UnWrapKey. For an application to use the key vault keys, it needs to authenticate using a token from the Azure Active Directory. For this we first need to register an application with azure active directory and then use the Application id and Authentication key(client secret) to authenticate against the AD application. Instead of using the key/secret, this could also be through a certificate authentication, which might be a more preferred approach(For the simplicity of this demo will use the application id and the secret directly). To connect to the AD application we can use the Active Directory Authentication Library nuget package, the KeyVault libraries are availalble as part of the samples.
var keyClient = new KeyVaultClient((authority, resource, scope) =>
{
var adCredential = new ClientCredential(applicationId, applicationSecret);
var authenticationContext = new AuthenticationContext(authority, null);
return authenticationContext.AcquireToken(resource, adCredential).AccessToken;
});
// Get the key details
var keyIdentifier = "https://testvaultrahul.vault.azure.net/keys/rahulkey/0f653b06c1d94159bc7090596bbf7784";
var key = await keyClient.GetKeyAsync(keyIdentifier);
var publicKey = Convert.ToBase64String(key.Key.N);
The application first uses the AD application credentials to authenticate and obtain the token for further interacting with the key vault. Using the key identifier that is available we get the details of the key.For performing the get operation the 'PermissionToKeys', should be set appropriately when registering the AD application, using Set-AzureKeyVaultAccessPolicy, against the key vault. Since this is RSA asymmetric algorithm, we have the public key available to us, and we can use this to encrypt the data or to verify the signature, locally in the application itself, though the vault client provides this for convenience.
using (var rsa = new RSACryptoServiceProvider())
{
var p = new RSAParameters() { Modulus = key.Key.N, Exponent = key.Key.E };
rsa.ImportParameters(p);
var byteData = Encoding.Unicode.GetBytes(textToEncrypt);
// Encrypt and Decrypt
var encryptedText = rsa.Encrypt(byteData, true);
var decryptedData = await keyClient.DecryptDataAsync(keyIdentifier, "RSA_OAEP", encryptedText);
var decryptedText = Encoding.Unicode.GetString(decryptedData.Result);
// Sign and Verify
var hasher = new SHA256CryptoServiceProvider();
var digest = hasher.ComputeHash(byteData);
var signature = await keyClient.SignAsync(keyIdentifier, "RS256", digest);
var isVerified = rsa.VerifyHash(digest, "Sha256", signature.Result);
As above, we use the public key available to create the [RSACryptoServiceProvider](https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/System.Security.Cryptography.RSACryptoServiceProvider(v=vs.110).aspx) to encrypt the data and also to verify the signature locally. So in an application we can encrypt the data locally and use the vault to decrypt it when required. Decryption can happen only from the vault, as the private key is only available in the vault, and does not cross the vault boundary.
With Azure Key Vault, managing keys and restricting application permission for keys can be easily managed and no information needs to be passed on to the developer or to any specific individual. Also the keys are secure behind the vault service and can also be protected using a HSM. You would need to update the application id and secret in the sample for it to work. Hope this helps in getting you started with Azure Key Vault.
Rahul Nath Newsletter
Join the newsletter to receive the latest updates in your inbox.
